A large and, above all, steadily increasing number of Industry 4.0 use cases require wireless communication on the production floor.
A large number of use cases already exist – let’s take a look at a few examples
Let’s take a look at the internal transportation of goods. Autonomous industrial trucks are increasingly taking over tasks here. Their task is, for example, to transport packaging units between production stations or to deliver empties. To do this, information about the order must be available and there must be communication with the loading bay in order to start the respective process. The term V2X – Verhicle to everything – is appropriate here.
Another application is the transmission of sensor data for the analysis and optimization of production (keywords “Big Data” & “Condition Monitoring”). Here too, data from sensors, some of which are installed temporarily, is indispensable.
Another example: asset tracking. This involves answering the question of where a particular semi-finished product, product or tool is currently located. Location data must be transmitted via mobile devices.
One last example to take it to the extreme – and of course to mention another buzzword: Smart Factory. Instead of a rigid production line, the aim is to find a flexible path through the finishing chain for each product. Ideally down to a batch size of one. And here too, the units must coordinate the next process steps, i.e. communicate wirelessly.
The requirements arise from the applications – first example of control
But what are the specific requirements for wireless communication technology? Let’s take another look at two examples, starting with the control of a process.
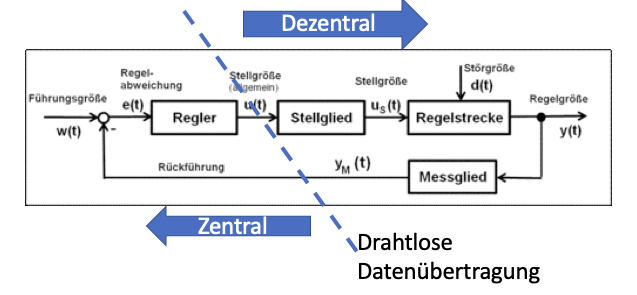
The system is decentralized and the control parameters are transferred in real time via the wireless interface. This results in a high degree of flexibility, which is interesting for packaging systems, for example.
The most important requirements in the control example are
- Latency
- Time required for information to travel from the source to the target
- Determines the maximum travel speed of the axes, as it is not possible to travel faster than the commands arrive
- Error rate
- Missing or corrupted packets must be repeated, we therefore also pay attention to the maximum speed
A second example of the requirements – data collection
A second example is the transmission of sensor data, e.g. for condition monitoring or the analysis of large data sets for process optimization.
Sensors for process parameters (temperatures, pressures, flow rate, etc.) or the system status (vibration, leakage, power consumption, etc.) can be transmitted. Both can be permanently installed or only temporarily equipped (system setup or troubleshooting).
The most important requirements in the data collection example are
- Range
- Distance of the sensors from the gateway
- Determines the cost of the installation; especially for large areas from outdoor use
- Number of devices
- Many devices need to be managed simultaneously
The requirements for communication technology differ significantly depending on the application
This is why there is hardly a single technology that meets all requirements, even if 5G with its different modes is preparing to do so.
Instead, different technologies exist side by side, as the following list shows as a small excerpt of the available technologies.
| Transmission rate | Latency | Typische Reichweite | Transmission power of the device | Examples in I4.0 | |
| LPWAN | Up to 600 Bit/s | >1 min | 15 km | > 0,025 W | Asset Tracking, Low-frequency sensor data |
| 4G | Up to 1 Gbit/s | 10 ms | 2 km / 10 km 3 | > 0,25 W | Telematics in agriculture (fill levels) |
| Wi-Fi | Up to 2,4 Gbit/s 1 | >7,6 ms2 | 300 m / 40 m 4 | > 1 W | Wireless terminal devices (torque wrenches) |
| 5G | Up to 10 Gbit/s | 1 ms | 15 km / > 1 km 5 | > 0,25 W | Closed-Loop-Control |
| 6G (geplant) | >1 Tbis/s | >1 ms | Tbd | Tbd | Fast-moving systems, autonomous driving, VR;AR |
: 2 Antennen, 802.11ax („Wi-Fi 6“)
2: Minimalwert aus Simulationsdaten mit 9 Clients, kann deutlich größer sein für „Wi-Fi 6“[8]
3: Je nach verwendetem Frequenzband in LTE [7]
4: im Freien / in Gebäuden
5: Je nach verwendetem Frequenzband in LTE [7]
If you want to know more about LPWAN, you can read this article.
Further development beyond 5G
6G is still at an early stage of development. Its introduction is planned for around 2030. The air interface used is also still open – RF or visible light; ground stations or satellites; or mixed forms of these.
The significantly stricter requirements compared to 5G are necessary, as not only the growth of devices/users is demanding its toll, but also the use cases that have not yet been (fully) implemented are being anticipated. These include virtual or augmented reality, autonomous driving or drone flights.
Sources
| [1] | V. S. Chakravarthi: Internet of Things and M2M Communication Technologies; Springer International Publishing; 2021 |
| [2] | J. Jasperneite, V. Lohweg (Hrsg.), Kommunikation und Bildverarbeitung in der Automation, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2020 |
| [3] | Schriegel, S.; Kobzan, T.; Jasperneite, J.: Investigation on a Distributed SDN Control Plane Architecture for Heteregenous Time Sensitve Networks. 14th IEEE International Workshop on Factory Communication Systems, 2018 |
| [4] | M. Gundall, J. Schneider, H. D. Schotten, M. Aleksy, D. Schulz, N. Franchi, N. Schwarzenberg, C. Markwart, R. Halfmann, P. Rost, D. Wübben, A. Neu- mann, M. Düngen, T. Neugebauer, R. Blunk, M. Kus, and J. Grießbach. 5G as Enabler for Industrie 4.0 Use Cases: Challenges and Concepts. In 23rd IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Au- tomation (ETFA 2018), Torino, Italy, 2018. |
| [5] | M. Božanic ́, S. Sinha: Mobile Communication Networks: 5G and a Vision of 6G, Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering 751, 2021 |
| [6] | Widya Tri Krisna Ayu: China has set up the 6G network, 8000 times faster than the 5G, seasia.co https://seasia.co/2020/11/23/china-has-set-up-the-6g-network-8000-times-faster-than-the-5g [Letzter Zugriff: 28.12.2021] |
| [7] | NN: LTE vs. 5G (Teil 4): Reichweiten, ENQT GmbH, Hamburg https://enqt.de/2020/11/ltevs5g-reichweiten/ [Letzter Zugriff: 03.01.2022] |
| [8] | NN: WLAN 6 (auch Wi-Fi 6) bewirkt große Veränderungen in kabellosen Netzwerken. Erhalte Antworten auf häufig gestellte Fragen zu den neuesten Funktionen und Verbesserungen, Intel https://www.intel.de/content/www/de/de/gaming/resources/wifi-6.html [Letzter Zugriff: 03.01.2022] |